Transnational Smart Specialisation Strategy for Baltic Sea Region (O2.1)
Trans-S3 for BSR is a formal, comprehensive and strategically-oriented document, developed in accordance with the Trans-S3 methodology adopted by the BSR partnership. Trans-S3 for BSR contains the main S3 priority areas / thematic domains, shared and agreed based on consultation by BSR stakeholders, which will be referred to when developing further programmes, projects and support instruments, including Transnational Innovation Brokerage System (TIBS) for BSR small and medium-sized enterprises.
The TIBS services further developed and expanded under the WP3 will prioritise SMEs from the selected S3 priority areas / domains, to increase their competitiveness and positions in global value chains/networks by innovation-based projects leading to greater internationalisation. This approach will intensify the chances of SBR SMEs and their innovation partners to succeed, and thus further materialise the opportunities attached to the selected S3 domains.
Trans-S3 for BSR will also serve as a sample application of the Trans-S3 methodology originated in the regular project and fine-tuned in the current project. As such, it will be used to promote S3 approach at the transnational/transregional context, specifically among the EU macro-regions.
TIBS services provided by more organisations and new SMEs supported in their progressed practical transnational ‘smart strategies’ (O3.3)
TIBS is a network of trained IIBs in the BSR that provide personal and practical help for SMEs to support innovations, strengthen their international efforts and guide their transnational cooperation offers. IIBs work is supported by a developed, improved set of specialized tools (including IT-tool) that elevated TIBS to a higher level.
TIBS was extended by new services providers. 2 organisations signed a declaration on joining TIBS.
During the project a lot of efforts was put by all PPs in recruiting new IIBs. In this process three separate induction packages have been developed and played a supportive role. 14 representatives of 7 new organisations was trained within the Induction Package 1 (IP1), which was in the form of introductory training for newly appointed IIBs from new project’s partners.
16 participants were trained within the Induction Package 2 (IP2), which was the specialised training course on innovation and internationalisation support and consultancy induction organised for IIBs from the TIBS network, including newly recruited members.
There are also new candidates willing to learn about TIBS within the Induction Package 3 (IP3). This training course is intended as an open-use Capacity Building package available for all organisations interested to take up TIBS services in the future. It consists of simple implementation guide, short training (standardised) e-course with a direct assistance allowed. The substantive content of the course covers with the content of IP1, but IP3 is meant mainly as a self-study tool. IP3 is available in the TIBS platform https://tibsnetwork.eu/ for organisations that fulfilled the declaration to join the TIBS (registration to the platform is required). IP3 is the main path to be a new member of TIBS.
The scope of TIBS influence was also extended to new entities. In the whole project 79 SMEs and other entities were directly assisted by TIBS services (16 from Podlaskie-PL, 13 from Vidzeme-LV, 6 from South Estonia-EE, 20 from Vilnius-LT, 9 from Kymenlaakso-FI, 5 from Northern Midsweden–SE and 10 from North Jutland–DK). See below.
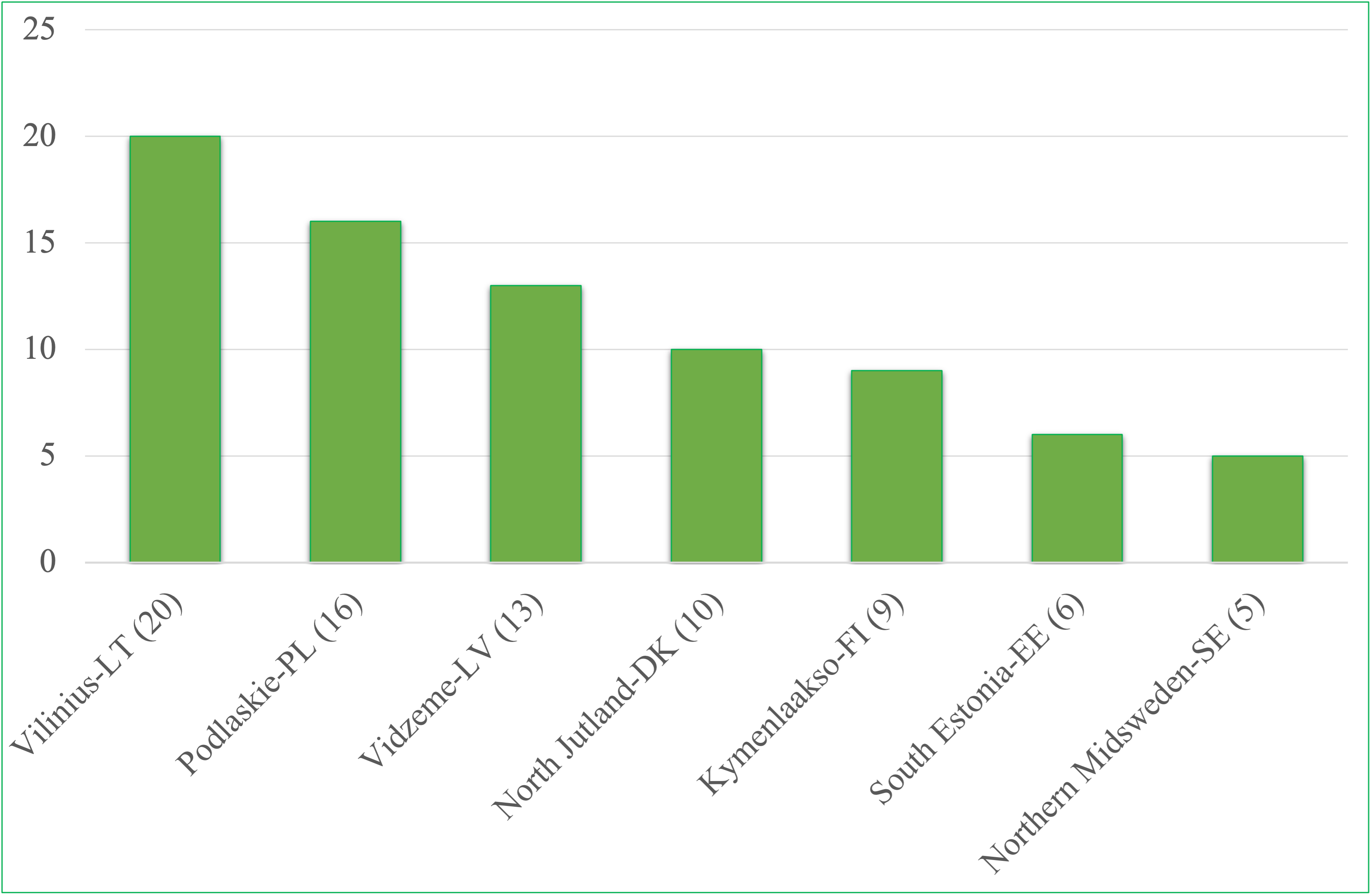
Needs of these companies were diagnosed, cooperation offers were developed and circulated, b2b matches were made. In these processes TIBS tools such as: F2 Value creation analysis for innovation form, F4(R4) Innovation cooperation offer, F6(R6) Innovation partners matching form were used. See below.
In total, 6 Joint Transnational Smart Strategies (JTSS) were developed between SMEs from PPs countries (1 LT-EE, 1 FI-PL, 1 PL-LV, 1 LV-EE, 1 EE-PL, 1 SE-LT).
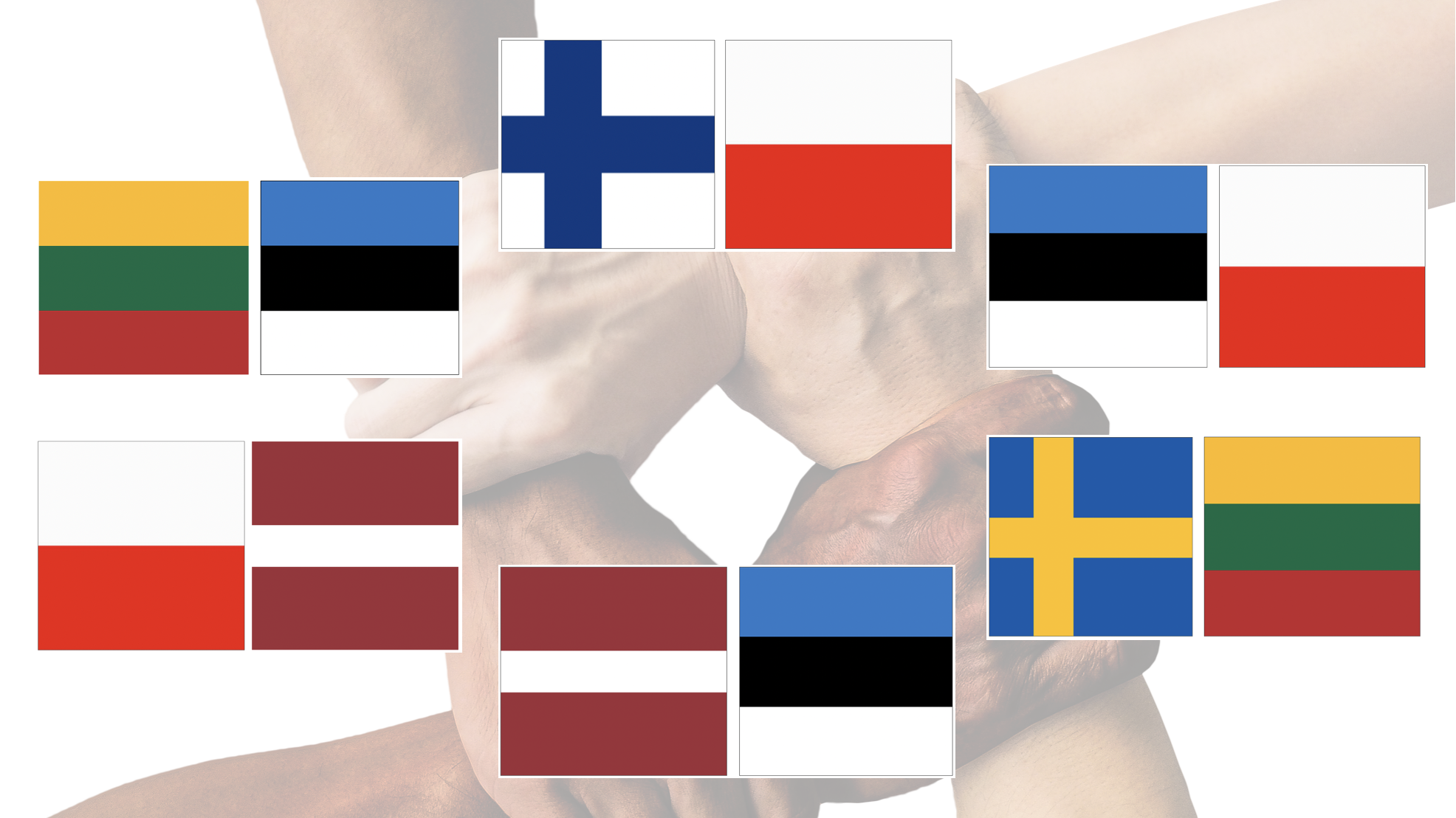
For creating JTSS the TIBS tool F7 Innovation partnership and JTSS establishment form was used. SMEs groups engaged in their JTSS enjoy benefits: increased institutionalised knowledge and competencies in innovation-intensive growth/internationalisation leading to more efficient use of human and technical resources. JTSS allows more effective searching and obtaining new financial resources by SMEs.



