Project Outputs
Transnational Smart Specialisation Strategy methodology finalized and disseminated (O.2.7)
The final Transnational Smart Specialisation Strategy (Trans-S3) priorities and domains were established by all Project Partners (PPs) during meeting in Hamburg on 23-24/10/2018. After the round table in Hamburg on 05/12/2018 and the policy round table in Brussels (20/02/2019) the Trans-S3 methodology was ready for dissemination.
The final methodology for Trans-S3 is presented in the publication: ‘Methodology for Transnational Smart Specialisation Strategy – Policy Paper’. The purpose of this document is to provide a general overview of the proposed methodology in a relatively short and simple form. This document is showing how transnational smart specialisations can be established and includes policy recommendations. The Trans-S3 methodology contain all necessary elements for replication by other future users.
In order the publication format to be reader- and user-friendly, we have launched the narrative in two different but related components:
– a general description of the methodology and recommendations (‘How to do it?’)
– specific application methods and conclusions drawn by us (‘As we have done’).
The final full version of the ‘Methodology for Transnational Smart Specialisation Strategy – Policy Paper’ is available on the project website (https://gosmartbsr.eu/publications) and on the official websites of the project partners.
The policy document, in two versions, full and abbreviated, was distributed by PPs to all interested stakeholders in regions inter alia via online portals and communication channels. Abbreviated version of the methodology and abstracts was disseminated also into national languages. In a few months from publication digital version has been downloaded/reached almost 400 recipients.
The full version of the document has also been published by Vidzeme Planning Region (VPR, PP3) in paper version (300 copies). Printout copies were delivered to all PPs, 60 of them will be disseminated at the Trans-S3 conference.
The Trans-S3 methodology was also a main content of GoSmart keynotes during Vidzeme Innovation Conference on 28/02/2019.
Transnational Innovation Brokerage System concept (O.3.6)
By the end of 30/09/2019 (4th Period) Transnational Innovation Brokerage System (TIBS) was ready to be market tested and be rolled out as a standard offer, additionally first pilot cycle of testing was conducted and completed. TIBS host structures are ready to manage the delivery of services, the staff and procedures.
Bialystok University of Technology (BUT, PP1) as a Lead Partner (LP) prepared (with support of the rest of PPs) methodology and tools developed on the basis of extensive market mechanism and market actors’ behaviours. Competent staff equipped with skills commensurate with the job demands and undergoing capacity building plans, was employed as International Innovation Brokers (IIBs). IIBs are competent and willing to work with business and Research & Development actors, additionally IIBs have completed a number of internal trainings about TIBS structure and methods. TIBS is coordinated by Lead IIB in cycles (Lead IIB is chosen among all IIBs by them, in first cycle (4th Period) Lead IIB was provided by Podlaskie Regional Development Foundation (PDRF, PP2), institutional support is also provided. TIBS methods and tools, which were define the process of service delivery to beneficiaries, cover all steps of the development and care of Joint Transnational Smart Strategies (JTSS) by trans-regional groups of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). TIBS host structures are ready to manage the delivery of services, the staff and procedures.
Target groups are invited to use TIBS services as described in other parts of the application and to progress their JTSS with the support available from TIBS. Activation of target groups, especially innovating and internationalising SMEs is achieved by other activities related to Trans-S3 identification (Work Package 2) and Communication & Visibility tools (Work Package 6).
Information on TIBS is prepared by PP3 (VPR) and available on project’s web page, and additionally regularly been posted to social media by all PPs, also disseminated among regional and local media to reach target audience. Events for entrepreneurs are used as a platform to meet potential TIBS users.
Transnational groups of SMEs with progressed practical Smart Strategies (O.4.6)
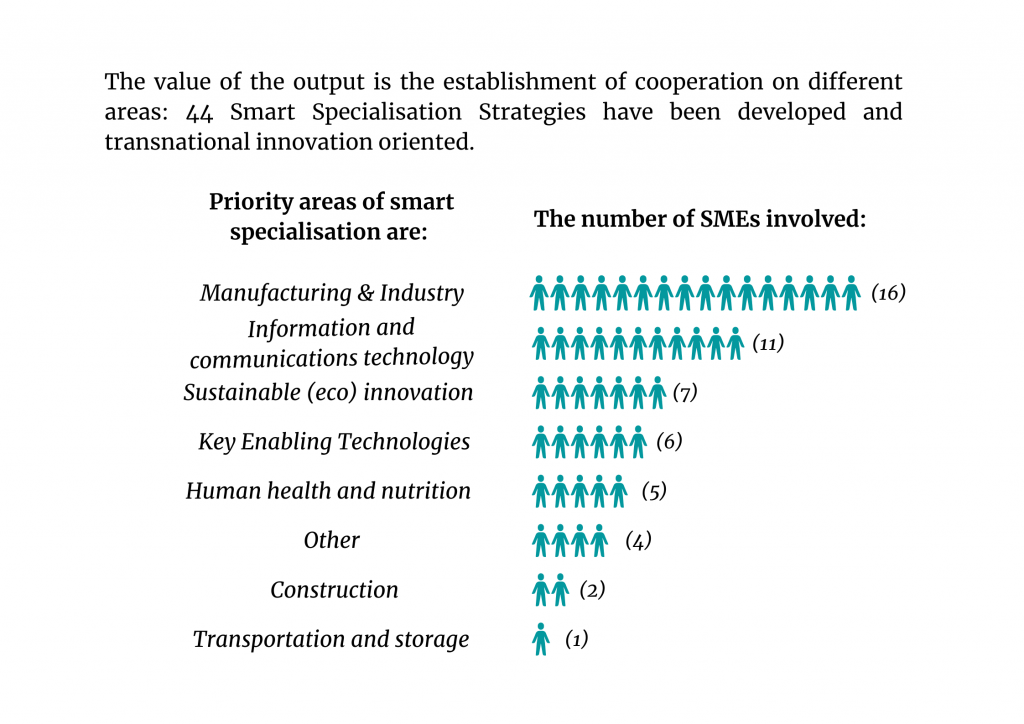
In total, 22 JTSS were developed between SMEs from PPs countries (in Application Form about 25-30 SMEs were planned). SMEs groups engaged in their JTSS enjoy many benefits, like increased institutionalized knowledge and competencies in innovation-intensive growth/internationalization, leading to more efficient use of human and technical resources: applied new processes or new technologies. JTSS allows more effective searching and obtaining new financial resources by SMEs, and finally SMEs learn how to collaborate in a transnational environment by pursuing JTSS related to innovation- and internationalization-based business models.
The most important and obvious obstacle in achieving higher JTSS indicator was the pandemic situation that broke the most intensive work on JTSSs. During the whole project 998 companies were contacted (see below).
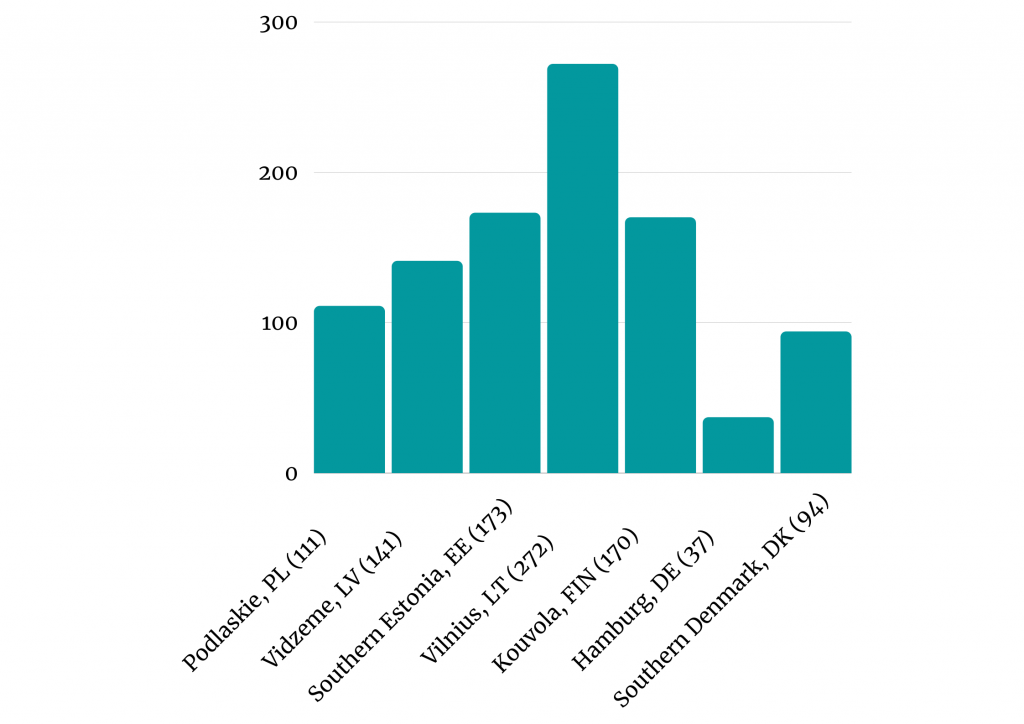
TIBS services were delivered to 296 pre-treated companies:
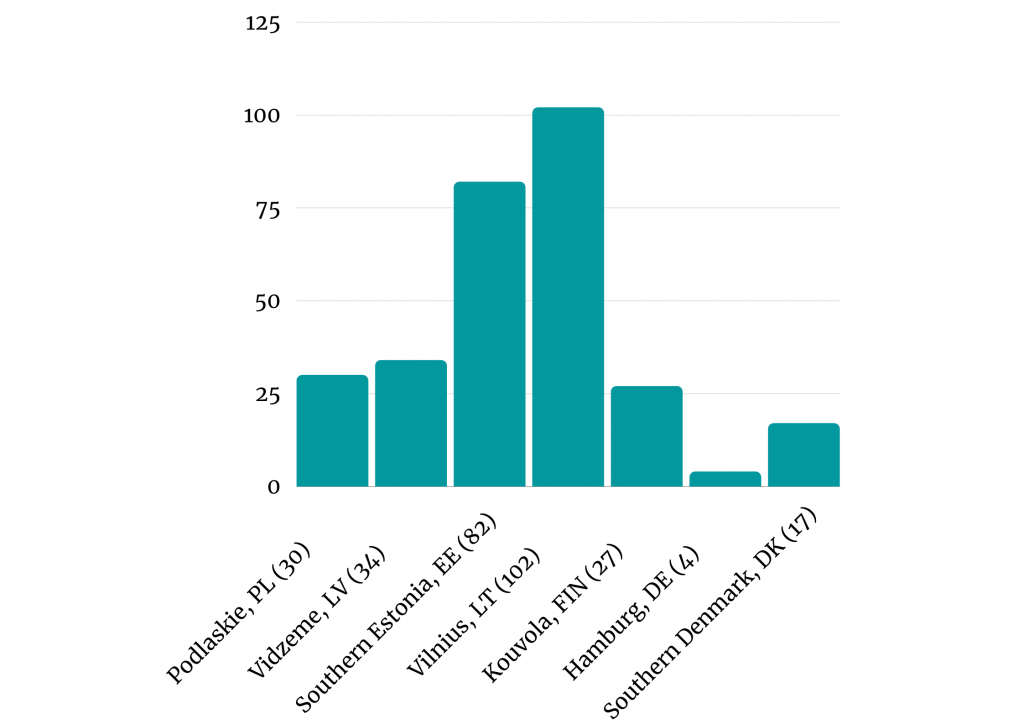
Despite achieving 116 matched SMEs (34 from Podlaskie, PL, 9 from Vidzeme, LV, 36 from Southern Estonia, EE, 13 from Vilnius, LT, 12 from Kouvola, FIN, 6 from Hamburg, DE, 5 companies from Southern Denmark, DK), it was hard to convince companies to benefits from developed JTSS, as the main problem was the general companies attitude to theirs market strategies focused on survival strategy, not on development strategy including also internationalization strategy.
All SMEs Smart Specialisations under implementation, resources for continuation of JTSS identified; TIBS service packs ready (O.5.1)
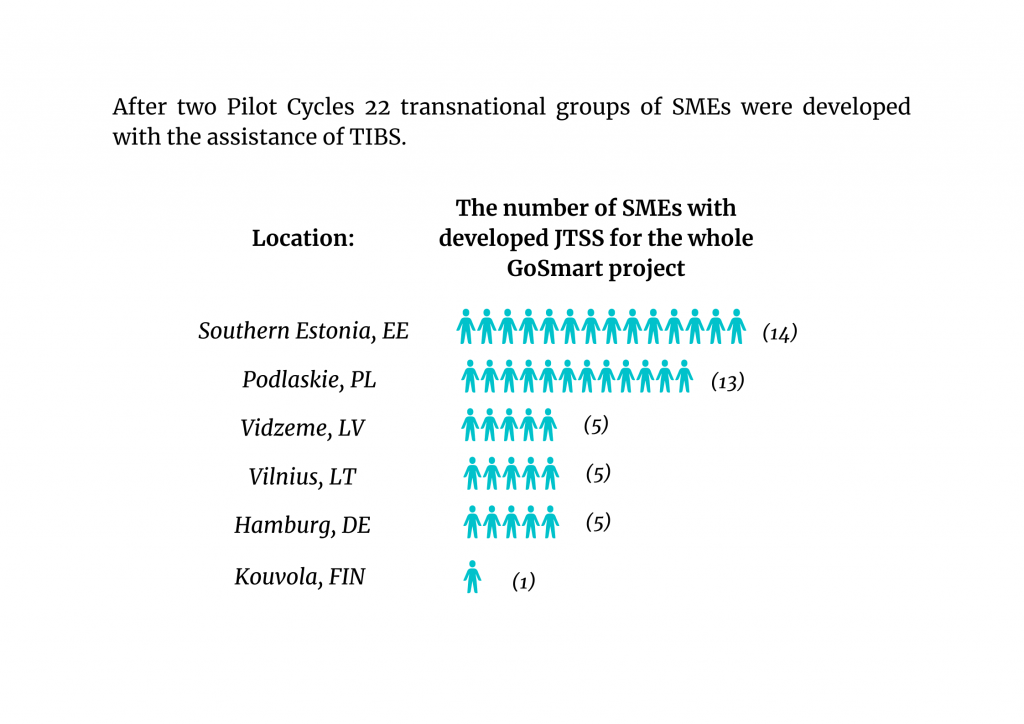
The overall aim of TIBS was to develop SME’s JTSS in the Baltic Sea Region in project target regions. The TIBS supported their growth and development in the regions through internationalisation of local businesses based on Smart Specialisation Strategies. After two Pilot Cycles, 22 transnational groups of SMEs were directly assisted by TIBS services.
The numbers of SMEs with developed JTSS for the whole GoSmart project are as follows: Podlaskie region (PL) reported in total 13 JTSSs, Vidzeme (LV) reported 5 JTSSs, Southern Estonia (EE) reported 14 JTSSs, Vilnius (LT) helped to initiate 5 JTSSs, Kouvola (FIN) reported 1 JTSSs and PP8 (HWWI) from Hamburg (DE) reported 5 JTSSs. SMEs from Southern Estonia (EE) and Podlaskie (PL) were most numerous.

Agreements on TIBS future (O.5.3)
The durability of the results of the project and the possibility of their use by the largest group of stakeholders was the subject of many meetings and discussions. In order to take the best decision regarding the future of TIBS, Feasibility Study for Continuation of TIBS was prepared. Three variants of the future TIBS were analyzed:
1 – TIBS as a structure within the Enterprise Europe Network (EEN),
2 – TIBS as an independent and commercially operating networking organization,
3 – integration of the TIBS system into another network organization operating for SMEs.
Based on the results of the analysis, considering the long-term durability of this system and the environmental conditions, the best chance for the effective provision of services for SMEs by TIBS is variant 1 – the inclusion of the TIBS system in the structure of the EEN. This option gives the opportunity to maintain and develop the unique properties of the services offered by TIBS and provides a wide access to potential customers.
The preliminary talks with EEN representatives on this subject were started. After the first presentation of TIBS for the EEN Steering / Sector Groups, positive comments and opinions were obtained and confirmation that the TIBS service has a chance to become one of the services offered by EEN.
The project will be continue under the name GoSmart & Excel BSR. Along with the decision to the extension, the strategy regarding the future of TIBS has been slightly changed. New partners involved in cooperation with SMEs are taking part in the continuing project. In the extension of the project, we primarily intend to develop the TIBS service, but also the functioning of the TIBS and JTSS systems. The development concerns both the use of IT tools and a larger geographic range.
The sustainable development of the TIBS system will allow it to operate as an independent system in the future. We intend to continue discussions on the possible inclusion of TIBS in the EEN.
TIBS sustainability plan under implementation (O.5.4)
The project has built TIBS, a knowledge-intensive, advanced and specialized SME support system, which effectively establishes new permanent structures business-science-authorities-nongovernmental for SME’s innovativeness sake.
The project is attended by: BUT (Podlaskie – PL) as LP and PPs: PRDF (Podlaskie – PL), VPR (Vidzeme – LV), Valga Municipality Government (Southern Estonia – EE), Public Institution Lithuanian Innovation Center (Vilnius – LT), Kouvola Innovation Oy (Kouvola – FIN), The Hamburg Institute of International Economics (Hamburg – DE), Business Aabenraa (Southern Denmark – DK).
Seven Innovation Brokers (one from each region) are involved in the operation of TIBS. In total, the dedicated staff of the project is 45 people in different levels of engagement. The project developed and implemented TIBS procedures in accordance with the adopted methodology. The following stages/pillars have been undertaken: (1) Management, (2) Developing TIBS, (3) Developing JTSS for innovation and internationalization & testing TIBS services, (4) Advancing JTSS for innovation and internationalization & making TIBS services sustainable, (5) Dissemination and proliferation of results & building ground for expanding TIBS.
TIBS services have been used by a significant number of innovating SMEs groups from different regions in the BSR. TIBS services have been tested in real market conditions thorough two intakes and processing cycles of beneficiary SMEs groups, assessed jointly by PPs, and prepared for sustainable continuation.
Comprehensive characteristics of TIBS existence and functioning, along with durability prospects are collected and made available through GoSmart BSR project monitoring and evaluation systems.



